티스토리 뷰
2019학년도 1학기 컴퓨터구조 중간고사 대비하여 정리했었던 내용입니다.
교재 = Computer_Organization_and_Design_5th_Edition
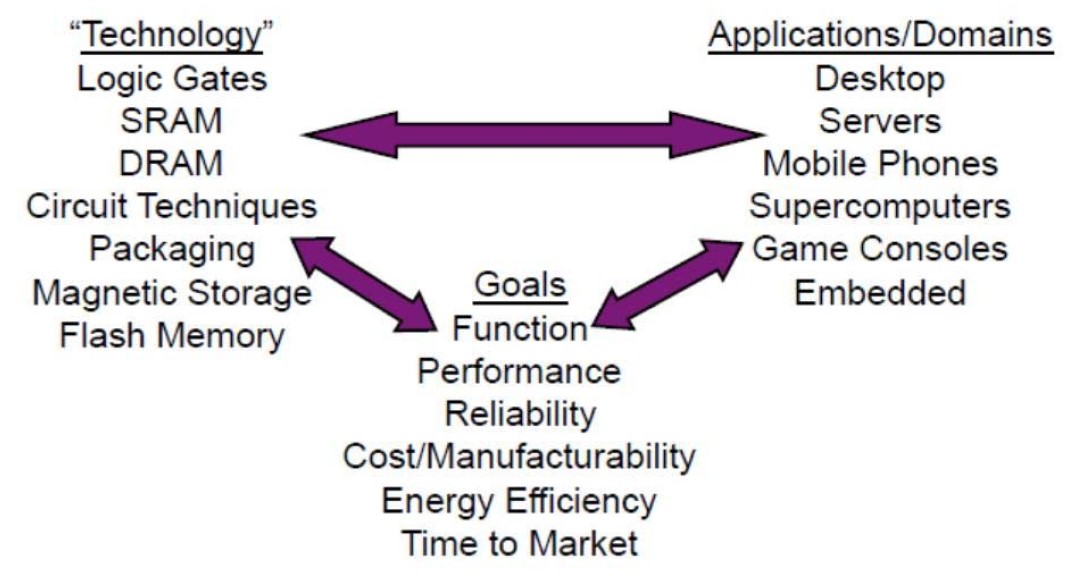
컴퓨터 설계의 목적과 제약조건 (Goals)
= 기능, 낮은 가격, 신뢰성, 저전력, 높은 성능, 앞 5가지 및 기타 등등의 균형
Applications/Domains
- Desktop
- Mobile: laptops, mobile phones
- Embedded: microcontrollers in automobiles, door knobs
Technology
- IC의 주요 부분 (평가 기준)
= 퍼포먼스, 신뢰성, 가격, 전력, 대량 생산 시설
l 무어의 법칙 = 반도체 메모리의 용량이나 CPU의 속도는 18~24개월마다 2배씩 향상된다. / 컴퓨팅 성능은 18개월마다 2배씩 향상된다. / 컴퓨터 가격은 18개월마다 반으로 떨어진다. (but 여러가지 문제(특히 발열) 때문에 2005년 이후부터 맞지 않는 말이 됨. – Single-Core => Multi-Core)
First Microprocessor = Intel 4004 (1971) – 10000nm, 108KHz, 4bit
Pinnacle(절정) of Single-Core Microprocessor = Intel Pentium4 (2003) – 90nm, 3.4GHz, 64bit
Modern Multi-Core Processor = Intel Core I7 (2009) – 45nm, 3.2~3.6GHz, 128bit, Quard-Core
l Modern Multi-Core Processor는 그냥 그런가보다 하고 넘어감.
Explicit Parallelism
- Multi-Threading
- Multi-Core
- GPU
컴퓨터 구조를 구상할 때에는 Goals, applications, technology 3가지를 모두 고려해야 한다.
CPU Performance
T = Tck * CPI * IC
l Tck = Cycle time in seconds (Tck = 1 / Clock Rate)
l CPI = Number of clock cycles per instruction
l IC = Instruction counts
l T = CPU using seconds for program
l MIPS = million instruction per second (= inst / exec * 10^6)
Performance = Execution Time!!!
l Elapsed Time = 전체 시간 (입출력 포함)
l CPU Time = 프로그램을 돌리는데 CPU를 사용한 시간 (입출력 제외)
성능 향상 = 실행시간 감소.
- Increase Clock Rate
- Decrease CPI
- Reduce IC
l 하나의 값이 바뀌면 다른 값에 영향을 줄 수 있다!
l 따라서 Clock Rate가 높다고, CPI가 낮다고, IC가 적다고 성능이 무조건 좋은 것은 아니다!
암달의 법칙 (f = 전체 중 성능개선이 된 부분%, a = f의 성능개선이 된 정도)

MIPS | ISA (*MIPS Processor와 million instruction per second는 다른 것!)
- Data types = word(32), byte(8), half-word(16), single FP(32), double FP(64)
Register Naming (개수 중요함!)
|
$zero |
Hardwired to 0. |
1개 |
|
$at |
Reserved for pseudo-instructions. |
1개 |
|
$v0, $v1 |
Results and expression evaluation. |
2개 |
|
$a0-$a3 |
Arguments. |
4개 |
|
$s0-$s7 |
Save Values. |
8개 |
|
$t0-$t9 |
Temporary values. |
10개 |
더 자세한 내용 (인터넷 자료)
|
Register No. |
Name |
Usage |
|
$0 |
$zero |
Hard-wired to 0 (0으로 고정) |
|
$1 |
$at |
의사 명령어 전용 |
|
$2-$3 |
$v0-$v1 |
Value. 함수 반환 값 ($v0는 syscall사용시에도 사용) |
|
$4-$7 |
$a0-$a3 |
Arguments. 매개변수 |
|
$8-$15 |
$t0-$t7 |
Temporary data. |
|
$16-$23 |
$s0-$s7 |
Saved registers. |
|
$24-$25 |
$t8-$t9 |
More temporary registers. |
|
$26-$27 |
$k0-$k1 |
Reserved for kernel. Do not use. |
|
$28 |
$gp |
Global Area Pointer (base of global data segment) |
|
$29 |
$sp |
Stack Pointer |
|
$30 |
$fp |
Frame Pointer |
|
$31 |
$ra |
Return Address |
|
$f0-$f3 |
- |
Floating point return values |
|
$f4-$f10 |
- |
Temporary registers, not preserved by subprograms |
|
$f12-$f14 |
- |
First two arguments to subprograms, not preserved by subprograms |
|
$f16-$f18 |
- |
More temporary registers, not preserved by subprograms |
|
$f20-$f31 |
- |
Saved registers, preserved by subprograms |
Instructions
- Arithmetic operations ex) add, addi, addu, …
- Data movement operations ex) lw, sw, …
- Control flow operations ex) beq, bne, j, jr, …
- Logical operations ex) sll, sra, and, or, …
The basic type of instruction has 4 components:
1. Operation name
2. 1st source operand
3. 2nd source operand
4. Destination operand
add $dst, $src1, $src2 # $dst = $src1 + $src2
sub $dst, $src1, $src2 # $dst = $src1 - $src2
l 음수의 표현 방식은 2의 보수가 가장 좋다. (1의 보수에 +1)
addi => src2 대신 상수를 사용하는 것이 가능. (i = immediate)
addu => 부호 없는 덧셈. (u = unsigned)
MIPS에서 Memory access 명령어는 load, store종류밖에 없다 => 속도상 이점
lw $dst, offset($base) # $base에 저장되어 있는 주소값 + offset만큼 더한 주소에서 word(32비트)만큼을 가져와 $dst에 저장.
sw $dst, offset($base) # 저장.
sll $dst, $src, num # shift left logical. $src의 비트를 왼쪽으로 num만큼 shift해서 dst에 저장한다. * $dst=$src*2num 가 된다.
beq $reg1, $reg2, label # branch equal. if ($reg1 == $reg2) goto label.
bne $reg1, $reg2, label # branch not equal. if ($reg1 != $reg2) goto label.
j label # jump (=goto). Jump to label.
slt $t0 $reg1, $reg2 # set less than. if ($reg1 < $reg2) $t0 = 1.
★beq와 slt의 조합으로 이상, 이하 조건문 작성 가능!
|
$s0 < $s1 |
slt $t0, $s0, $s1 bne $t0, $0, Less # if ($s0 < $s1) goto Less |
|
$s0 > $s1 |
slt $t0, $s1, $s0 bne $t0, $0, Grtr # if ($s0 > $s1) goto Grtr |
|
$s0 >= $s1 |
slt $t0, $s0, $s1 beq $t0, $0, Gteq # if ($s0 >= $s1) goto Gteq |
|
$s0 <= $s1 |
slt $t0, $s1, $s0 beq $t0, $0, Lteq # if ($s0 <= $s1) goto Lteq |
bltz $src, label # branch on less than zero. goto if ($src < 0)
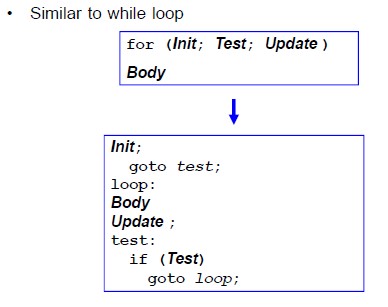
단순한 코드를 위한 반복문의 표현

System calls
|
Service |
System Call Code |
Arguments |
Result |
|
print integer |
1 |
$a0 = value |
|
|
print float |
2 |
$f12 = float value |
|
|
print double |
3 |
$f12 = double value |
|
|
print string |
4 |
$a0 = address of string |
|
|
read integer |
5 |
$v0 = value read |
|
|
read float |
6 |
$f0 = value read |
|
|
read double |
7 |
$f0 = value read |
|
|
read string |
8 |
$a0 = buffer, $a1 = length |
|
|
memory allocation |
9 |
$a0 = amount |
$v0 = address of block |
|
exit |
10 |
|
|
|
print character |
11 |
$a0 = integer |
|
|
read character |
12 |
|
char in $v0 |
MIPS Assembler Directives
- .asciiz = null로 끝나는 문자열 저장
- .data = 데이터 영역 시작
- .text = 텍스트 영역 (함수 등) 시작
- .global = 밖에서 주 기호에 접근할 수 있음.
- .word = word단위로 메모리에 저장.
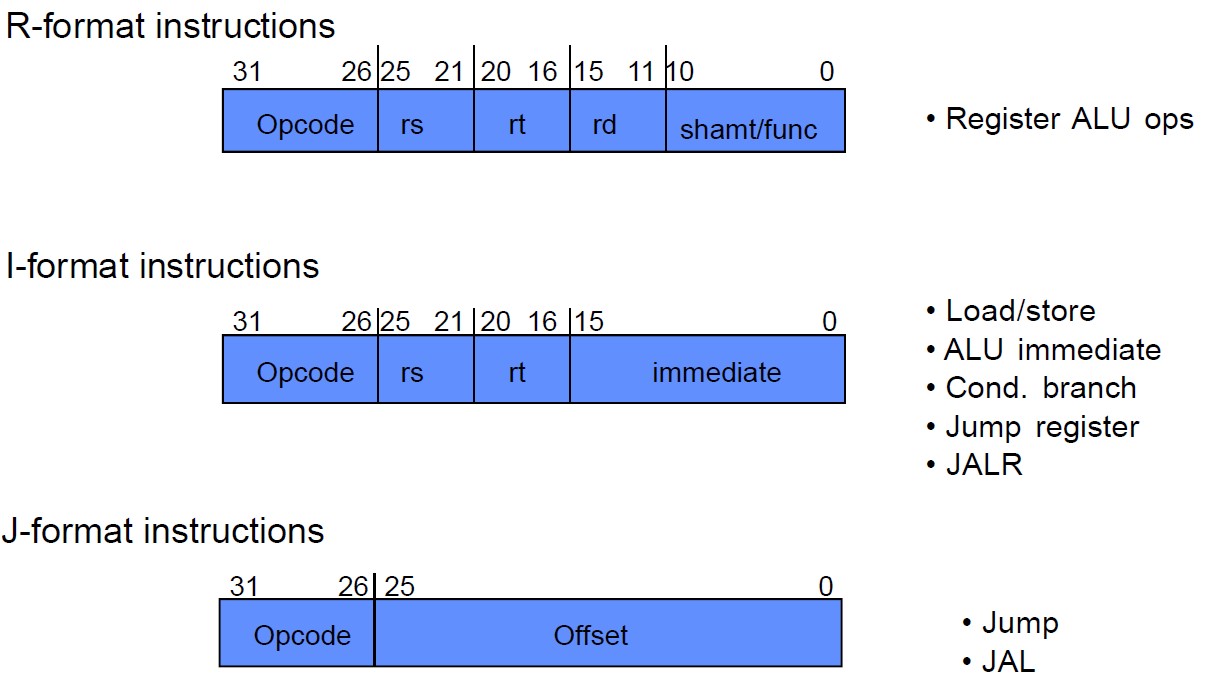
MIPS 명령어의 3가지 포맷
- R-format => register
- I-format => immediate
- J-format => jump
프린트할 목적으로 워드에 먼저 적고 복붙했는데 엄청 이상하게 나왔다.. 귀찮으니 그냥 둬야지.. 그림하고 수식도 복붙 안된거 따로 넣느라 귀찮았당
'공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| OSI 7 Layer table update(2019.06.09) _update device (0) | 2019.06.09 |
|---|---|
| 2019학년도 1학기 데이터통신 중간고사 대비 정리 (0) | 2019.04.16 |
| [GNOME Project] Calculator 빌드 방법 (0) | 2018.11.23 |
| GNOME Calculator 오픈소스 프로젝트 개발 환경 구축 순서 (0) | 2018.10.31 |
| 1 - (3,4) 추상 자료형과 알고리즘의 성능 분석 (작성中) (0) | 2018.07.26 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 알고리즘
- LG
- DFS
- 동적 계획법
- c++
- 오픈소스
- PyPy3
- c
- 정렬
- 백트래킹
- BFS
- 플로이드 와셜
- Dynamic Programming
- 백준
- webOS
- 프로그래머스
- 카카오
- BaekJoon
- 코딩
- 이분탐색
- 1932
- 인공지능
- 구현
- 한화큐셀
- 피보나치
- 완전탐색
- 파이썬
- DP
- 브루트포스
- 컨트리뷰톤
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |

 중간고사 대비 정리.docx
중간고사 대비 정리.docx